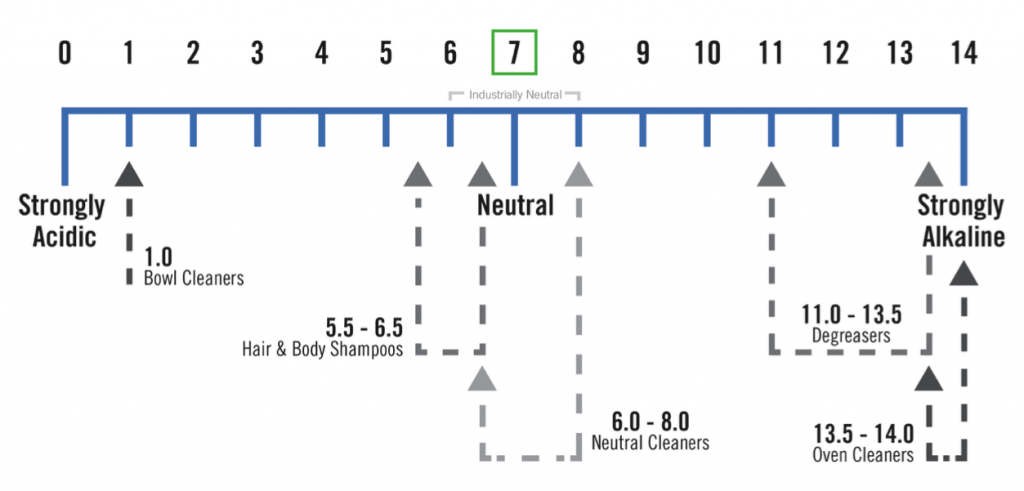
As almost all cleaning professionals know, there are three terms that apply to chemicals used in cleaning: acid, alkaline, or neutral. The pH scale ranges from 1 to 14 and is a measure of a solution’s acidity or alkalinity. A pH of 7 is neutral; a pH less than 7 is acidic; and a pH greater than 7 is alkaline, or basic.
Various categories of cleaners are formulated by manufactures as acidic or alkaline because of their effectiveness in cleaning or dissolving certain soil types. Oven cleaners, for example, are formulated to be strongly alkaline because alkaline solutions are effective at breaking down baked-on protein, fatty soils, and the types of carbonized soils often found in and on dirty ovens. Toilet cleaners, on the other hand, tend to be acidic for dissolving water scale and rust.
The Relative Safety Concerns of High And Low pH Chemicals
Safety is a relative term. It can be evaluated on a number of fronts including: acute toxicity concern from immediate contact with a cleaner; long-term human health exposure; safety for the environment; safety for surfaces cleaned; building safety measures such as odor sensitivities of occupants